Recently, the group of Prof. SUN Daofeng from China University of Petroleum made significant progress in multi-component metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based on porphyrin and Rear-Earth, cooperating with prof. ZHOU Hongcai from Texas A&M University. The paper, titled “Pore-Environment Engineering with Multiple Metal Sites in Rare-Earth Porphyrinic Metal–Organic Frameworks”, has been published by Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. ZHANG Liangliang, YUAN Shuai, and FENG Liang are co-first authors. Prof. SUN and ZHOU are corresponding authors and China University of Petroleum is the first corresponding affiliation.
Multi-component metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with synergistic functionalities in a designed cavity are particularly interesting because of their potential applications in gas adsorption, separation, cooperative catalysis, and biomimetics. Pioneering work has been demonstrated by Yaghi and co-workers by incorporating up to eight functional groups into multivariate MOFs (MTV-MOFs), which showed emergent properties distinct from their parent frameworks. However, this method typically lacks a high level of control over the positions of functional groups as functional groups tend to be disordered in the crystal lattice. To address this issue, Tefel and coworkers demonstrated a strategy to incorporate different functional groups on linkers of various connectivity and symmetry in pre-determined positions of a mixed-linker MOF. Still, this strategy only works for a limited number of MOFs, which require linkers with exactly-matched sizes and symmetries. Later on, our group introduced a post-synthetic method, linker installation, to engineer pore environments with precisely placed linkers in zirconium MOFs. However, it is still challenging to incorporate multiple metal sites in pre-determined positions within a MOF cavity.
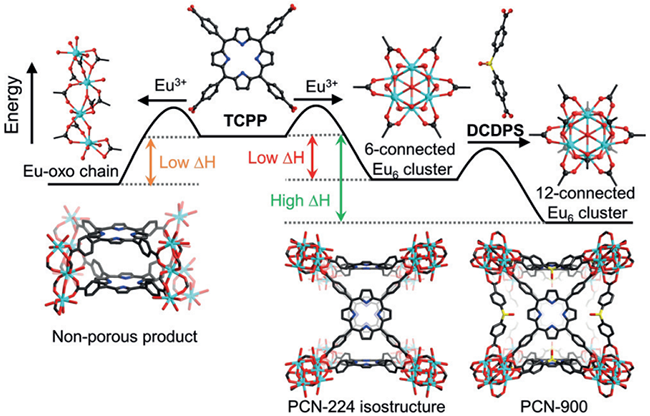
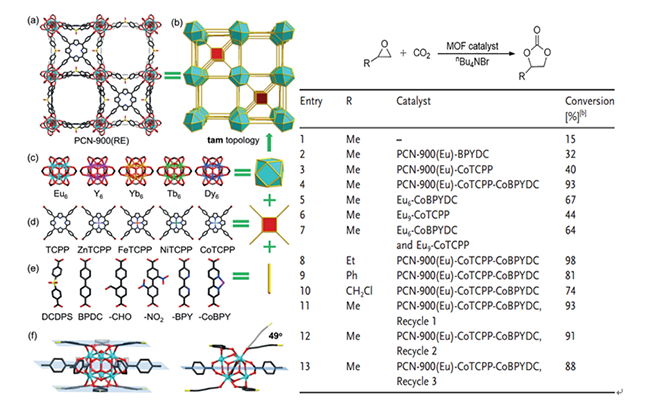
Herein, we assembled a series of multi-component RE-MOFs, namely PCN-900(RE), using a combination of tetratopic porphyrinic linkers, linear linkers, and RE6(OH)8(COO)12 clusters. Pore environment engineering with multiple metal sites was realized in these MOFs, which led to the formation of mesopores decorated by high-density metal sites. Furthermore, PCN-900(RE) represents an ideal platform for heterogeneous catalysis. As a proof of concept, we explored their catalytic performances in the cycloaddition of CO2 and epoxides.
Angewandte Chemie, with its excellent Impact Factor of 11.994 (2016), is maintaining its leading position among the general chemistry journals. It appears weekly in a highly optimized, reader-friendly format; new articles appear online almost every day. It is one of the prime chemistry journals in the world, with an Impact Factor higher than those of comparable journals.
The research interests of Prof. SUN Daofeng focus on functional order porous materials, including self-assembly of metal-organic supermolecular, MOF membrane, porous carbon materials, Li ion battery and so on. The group of Prof. SUN has published numerous articles on famous journals including Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Chemical Communications, and Chemistry A European Journal.
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201802661
Source: School of Science
Updatetime: 2018-06-06