Recently, the paper Observation of Internal Photoinduced Electron and Hole Separation in Hybrid Two-Dimentional Perovskite Films was publised by JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY. It was co-finished by prof. Zhang Jun's group from School of Chemical Engineering and Jin Shengye's group from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The first author is Liu Junxue, a doctor candidate from School of Chemical Engineering.
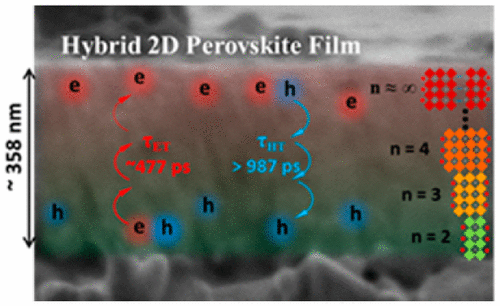
Two-dimensional (2D) organolead halide perovskites have recently emerged as an attractive material for applications in photovoltaics and other optoelectronic devices. Recent reports have demonstrated that the 2D multi-layered perovskite films actually comprised multiple perovskite phases (with various n values from 1, 2, 3 and 4 to near ∞), even though the films were intended to be prepared as a single-phase. This hybrid feature seems to be ineluctable in fabricating 2D films. However, two important questions remain yet-to-be-answered: first, how the different perovskite phases align in the hybrid films; second, whether the band alignment between different phases induces energy funneling or instead charge separation. The latter is especially important because it dictates the application of these hybrid 2D perovskite films: energy funneling is useful for light-emitting applications, whereas charge separation would be more beneficial for light conversion or detection.
The research group led by Prof. Zhang Jun cooperating with Prof. Jin Shengye from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics studied the charge carrier dynamics in 2D perovskite films, using ultrafast transient absorption and time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy. Researchers found that indeed multiple perovskite phases with various n values co-existed in the 2D perovskite films, and more interestingly, these perovskite phases were naturally aligned in the order of n along the growth direction perpendicular to the substrate. Driven by the built-in band alignment between different perovskite phases, consecutive internal electron transfer from small-n to large-n perovskite phases and hole transfer in the opposite direction were observed in a film of ~358 nm thickness. This unique self-charge-separation property of the 2D perovskite films can facilitate their applications in photovoltaics and other optoelectronics devices.
The findings recieved a high opinion from the peer reviewers. It is of great importance to the development of optoelectronic devices and the field of perovskite.
See more about the paper: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.6b12581
Editor: Bu Lingduo Source: UPC News Center